Table of Contents
Introduction
A cyberattack can cripple your data center, a natural disaster can wipe out your servers, or a simple software glitch can throw your system into chaos.
Such situations can be terrifying, leading to panic and decreased productivity, all while your revenue takes a nosedive. Sounds like a nightmare, right? But what if your business can keep humming even amidst such significant disruptions? Azure disaster recovery offers a lifeline among all these challenges! With ADR, companies can rest assured that their operations are safe against unforeseen events.
Recent reports indicate, “The global disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS) market was valued at USD 11.27 billion in 2023 and expects to grow at a CAGR of 27.0% during the forecast period, highlighting the rising importance of resilient disaster recovery solutions in modern business environments.”
What is Azure Disaster Recovery?
Disaster Recovery in Azure is a solution provided by Microsoft Azure to help businesses protect their data and applications from unexpected outages or disasters. It enables organizations to create and maintain copies of their critical applications and data in Azure, providing a failover option in case their primary systems become unavailable due to various reasons such as hardware failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks. This service offers features like automated failover, continuous replication, and recovery orchestration, helping organizations minimize downtime and ensure business continuity.
Note: Organizations can explore Azure Disaster Recovery pricing options based on their specific requirements and SLAs.
Need For Azure Disaster Recovery
Azure Disaster Recovery is essential for addressing unavoidable situations that demand preparedness, such as:
🟠 Natural Calamities
Natural disasters can damage on-site data centers, causing data loss. Azure’s distributed data centers offer backup locations to ensure data accessibility during disasters.
🟠 Man-Made Disasters
Man-made disasters like power outages, cyberattacks, or accidental data deletion disrupt business. Azure’s features, like data replication, backup, and failover capabilities, enable quick recovery and business continuity.
🟠 Global Reach
Businesses with global operations need continuous service access despite localized disruptions. Azure’s global network enables seamless data and application replication across regions, ensuring uninterrupted access even during local disruptions.
🟠 Regulatory Compliance
Numerous industries impose rigorous regulatory mandates on data protection, privacy, and disaster recovery procedures. Azure provides compliance certifications, adheres to industry standards to meet regulatory obligations, and avoids data breaches or downtime penalties.
🟠 Cost-Effectiveness
Establishing and maintaining an on-premises disaster recovery infrastructure may incur significant expenses and demand substantial resources. Azure’s pay-as-you-go model minimizes upfront capital expenditures and operational costs for disaster recovery infrastructure.
🟠 Testing and Validation
Azure offers tools and services for testing disaster recovery planning without disrupting production. It enables organizations to simulate different disaster scenarios and ensure the effectiveness of their strategies.
Benefits of Disaster Recovery In Azure
In addition to reduced downtime, enhanced business resilience, and cost-effectiveness, Disaster Recovery in Azure offers significant advantages like:
- Continuous Data Protection (CDP): It guarantees minimal data loss through replication with real-time alterations.
- Granular Application Recovery: It allows for the selective recovery of specific application components or tiers during failover.
- Azure Resource Manager (ARM) Integration: Achieves simplified deployment and management of resources through ARM templates, streamlining configuration, and orchestration.
- Cross-Platform Flexibility: You can use Azure Disaster Recovery to save both virtual and physical servers, no matter what type of computer they run on.
- Automated Network Configuration: It also automates network setup during failover, ensuring seamless connectivity without manual intervention.
- Testing without disruption: You can test your disaster recovery plan without disturbing your actual work, ensuring everything will work if there’s a problem.
- Application-Aware Recovery: Understanding dependencies between application components ensures consistent recovery and minimal downtime.
- Multi-Site Orchestration: If you have more than one place to keep copies of your data, Azure Disaster Recovery can ensure they all work together, giving you extra backup in case one fails.
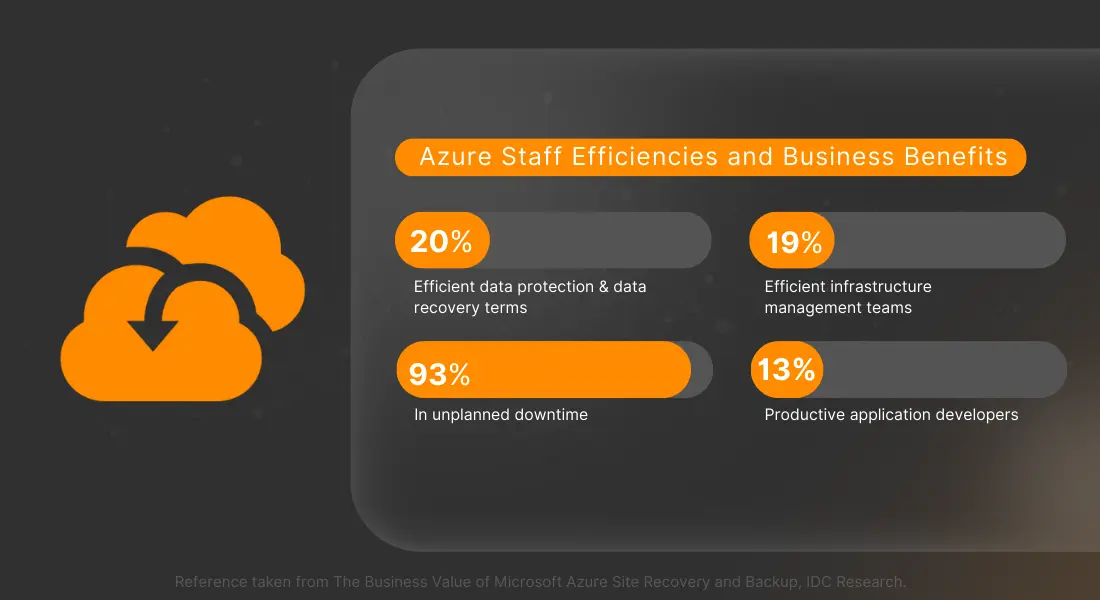
Azure Disaster Recovery Solutions
Here are some of the most common Azure backup and restore options to look forward to:
1. Azure Site Recovery
Azure Site Recovery is a custom-built disaster recovery solution provided by Microsoft that functions seamlessly in the cloud environment. It safeguards your data and applications by replicating them to a backup location in the cloud data centers. You can switch to this backup location quickly during an outage, ensuring your applications and data continue running with minimal disruption.
ASR, part of Azure’s Disaster Recovery-as-a-Service(DRaaS) offerings, is suitable for both cloud and hybrid cloud setups. It maintains nearly real-time replication of your data to ensure synchronization. Its application-consistent snapshot feature ensures your data remains usable even after switching to the backup site. This service allows you to use ‘Azure’ as a disaster recovery site without requiring extra infrastructure investment. Besides, you pay for what you use, making it a cost-effective solution for disaster recovery needs.
For whom is Azure Site Recovery specifically designed?
- Enterprises requiring to comply with specific data regulations and protection standards will find Azure disaster recovery helpful in managing compliance and protecting sensitive data.
- Organizations relying on outdated disaster recovery solutions can substantially benefit from using Azure disaster recovery solutions.
- Businesses specifically from Finance, Healthcare, Retail, E-commerce, Manufacturing, and Government industries relying heavily on applications for their daily operations can save their mission-critical operations using Azure disaster recovery solutions.
In what situations is Azure Site Recovery applicable?
- Copying Azure VMs from one Azure region to another.
- Replicating on-premises VMware VMs, Hyper-V VMs, physical Windows and Linux servers, and Azure Stack VMs to Azure.
- Replicating on-premises VMware VMs, Hyper-V VMs administered by System Center VMM, and physical servers to a backup location.
- Replicating specific workloads running on supported machines.
Models in Azure Site Recovery
A. Disaster Recovery Within Azure to Azure
It’s a backup and recovery service within Azure. It ensures your data and applications can quickly switch to another Azure region if there’s a problem, keeping your business running smoothly.
Note: ASR works only between regions in the same cluster. Refer to the documentation for details. Also, replicated VMs must run on supported OS like Windows or Linux.
⮕ Key components
- Source VMs: Azure VM instances in the original region.
- Source VM Storage: The disk storage associated with those VMs.
- Source VM Networks: Virtual networks and subnets housing the VMs.
- Cache Storage Account: A storage account within the same network, temporarily holding VM changes.
- Target Resources: Resources set up for replication and failover, typically managed by Site Recovery but customizable.
⮕ Snapshots and Recovery Points
Snapshots are like screenshots you take but for virtual machines. They capture the state of your virtual machine’s disk at a specific moment. Site recovery uses these snapshots to create recovery points like bookmarks in time. If something goes wrong, you can return to these recovery points to restore your virtual machine to a safe and stable state, ensuring your data isn’t just lost or corrupted.
⮕ Replication Process
1. The system first adds a Site Recovery extension to the Virtual Machine.
2. It starts copying data to temporary storage called the Standard cache storage.
3. Site recovery moves the data to replicated disks or a storage account.
4. It takes regular “snapshots” of the virtual machine every 5 minutes, ensuring you have recent backups consistent with the apps running on the VM.
⮕ Failover
Failover is the switch from the central system to a backup to ensure smooth operation during an issue. With Azure Recovery Site, initiating failover creates a virtual machine in the backup location using the network and setting that you’ve chosen. It uses data copied from the central location to keep everything running without interruption.
Hire Azure developers to leverage Azure Disaster Recovery, unlock exclusive resilience for your business, and ensure unparalleled protection and continuity today!
B. Disaster Recovery From Physical Server to Azure
Physical Server to Azure DR with Azure Site Recovery involves replicating on-premises physical server workloads to Azure.
⮕ Key components
- Azure Subscription and Network: Transfer data from your physical machines to disks within your Azure subscription. Azure creates Virtual Machines from this data in your chosen network during failure.
- Process and Configuration Server: Like a central hub, it accepts data from local machines, applies compression and encryption, and then forwards it to Azure storage to manage replication.
- Master Target Server: On-premise server sending replicated data back to your local data center during a failback.
- Mobility Service: Installed on each machine for Azure replication. Microsoft advises automatic installation from the process server, but manual installation is possible.
⮕ Replication Process
1. Establish a deployment incorporating local and Azure components: The Recovery Services Vault designates the replication source and destination, configures a server, defines a replication policy, and activates replication.
2. ASR replicates initial server data to Azure storage using a predefined strategy.
3. ASR starts copying incremental changes to Azure after initial copy completion, tracked via.HRL log file.
4. Reroute traffic to Azure machine via Internet or Azure ExpressRoute with public peering.
⮕ Failover Process
1. Select the virtual machine for migration to Azure.
2. Choose a recovery point:
- “Latest” for the most recent data, but possibly not fully processed.
- “Latest processed” for quick migration, even if data processing is incomplete.
- “Latest app-consistent” for data integrity assurance.
- Custom” for manual recovery point selection.
3. You may shut down the source machine before migration, but it’s not obligatory.
4. Initiate the migration process and monitor progress via the Azure Site Recovery Jobs page.
5. Post-migration, validate the new VM and finalize the migration, removing other recovery options.
Post-Azure migration, consider re-replicating VMs back to the original site as necessary, referring to documentation for detailed instructions.
Note: To bring your data back from Azure using ASR, you need a local VMware setup, even if you initially protected physical machines. ASR can solely restore data to VMware VMs within your on-premises data center.
⮕ Failback Process
When your main site is back online, you can return your data from Azure using ASR. In the ASR console, choose the VM you want to bring back and request a “failover” from Azure.
1. Select the recovery point you want to use – it’s best to go with the latest one, even though you might lose some recent data.
2. Azure VMs shut down during the failover process, and your on-premises VMware VMs start up. It might cause some downtime.
3. Once the failback is complete, a job removes the Azure VMs that are no longer needed. Make sure the VMs shut down properly.
For more details and tips on speeding up the process, check out the Azure documentation.
2. Azure Backup
It is a centralized backup service solution to safeguard against ransomware threats. It regularly creates backups and stores them securely in the cloud, allowing you to restore specific data in case of accidental deletion, corruption, and other incidents. With a simple interface, you can set up backup plans for different kinds of data, like virtual machines, databases, and file shares, all in one place.
Look at all the benefits this service offers:
- Centralized Management to back up tasks easily from one place
- Supports backup and restore with application consistency for Windows (using VSS) and Linux (using scripts).
- Backups Multiple-Workload, including Azure Virtual Machines, on-premises servers, SQL Server, SAP HANA, Azure Files, and Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
- Offers storage in LRS, GRS, and ZRS for resilience and redundancy.
- Implements RBAC, soft delete, multi-user authentication, customer-managed keys, private endpoints, and redundancy for data protection.
- Cut costs by optimizing storage, using cheaper options for long-term backups, and only backing up what you need.
- Covers various infrastructure, databases, and storage workloads, including Azure VMs, SQL Server, SAP HANA, Azure Database for PostgreSQL, Azure Disks, Azure Files, and Azure Blob Storage.
3. Azure Archive Storage
Azure Storage Archive is a service designed for securely storing data that is infrequently Azure Storage Archive is a service designed for securely storing infrequently accessed data. It offers a cost-effective solution for retaining data that doesn’t require frequent access but needs to be stored for compliance access.
Look at the bonuses you get with this backup service,
- Data is securely transferred and stored with HTTPS and 256-bit AES encryption, meeting compliance requirements for sensitive data.
- Blob-level tiering enables easy management of storage tiers, allowing seamless transitions between storage classes for optimal data organization.
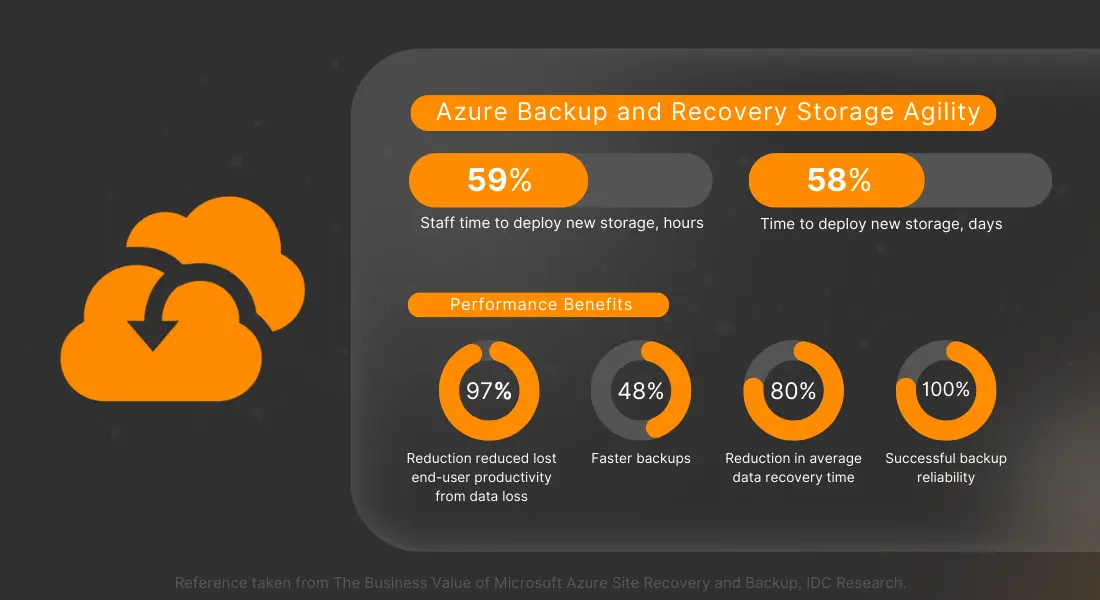
Best Practices For Disaster Recovery In Azure
Take a sneak peek into the Azure Disaster Recovery best practices:
Azure Disaster Recovery Plan
Test and implement your disaster recovery plan thoroughly to ensure effectiveness, incorporating necessary technologies within your SLA to restore functionality. Work on the following:
- Assess the impact of application failure & data loss to prioritize critical elements. Assign a dedicated owner for testing and automation.
- Be clear about the support contract procedures & escalation instructions to minimize downtime. Utilize cross-regions for critical applications.
- Automate backup strategies and document processes.
- Configure monitoring and alerts for all Azure services used. Train staff and conduct regular disaster recovery simulations for verification and improvement.
Operational Readiness Testing
Before implementing your Disaster Recovery plan, conduct operational readiness tests to reduce risks and verify the effectiveness. It includes:
1. Failback to the primary region
2. Failover to the secondary region
These tests ensure the synchronization of application-dependent services during the recovery process and identify any challenges related to operational and system changes affecting failback and failover functions, avoiding potential issues in real-world scenarios.
Dependent Service Outage
Ensure that Security Optimization Assessments are conducted to assess the implications of disruptions on dependent services. Monitor application responses during disruptions and evaluate Azure services individually to improve their availability and resilience. Finally, strengthen the Azure disaster recovery plan in Azure accordingly.
Network Outage
Network unavailability can hinder access to applications and data. Ensure that your Disaster Recovery Plan outlines procedures for network outages. Respond by operating essential applications with limited features or failing over to another region to minimize application downtime.
Plan For Regional Failures
To prepare for regional failure, Azure has two divisions, logically and physically, into units, referred to as regions. Each comprises multiple data centers, some with availability zones for added resilience during outages. Understand these divisions and utilize multiple areas to prepare for regional failures.
Conclusion
Azure Disaster Recovery, when coupled with Azure Managed services, offers a reliable solution for businesses to maintain operations in the face of unforeseen disruptions. Organizations can minimize downtime and ensure business continuity by leveraging Azure’s capabilities for data replication and rapid recovery. Thus, businesses can confidently navigate any crisis and embrace Disaster Recovery in Azure to survive and thrive in an ever-evolving world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective) is how quickly systems need to restore disaster recovery in Azure.
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective) is the maximum data loss allowed in Azure disaster recovery.
The maximum retention of Azure Site Recovery is 15 days.
Azure Disaster Recovery provides encryption, access controls, and audit logs to ensure data security and compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
ROI is measured based on reduced downtime, improved productivity, minimized data loss, and potential cost savings compared to traditional disaster recovery solutions.
Yes, Azure Disaster Recovery supports integration with various third-party applications, APIs, and tools, enabling seamless interoperability with your existing IT ecosystem.
Your Success Is Guaranteed !
We accelerate the release of digital product and guaranteed their success
We Use Slack, Jira & GitHub for Accurate Deployment and Effective Communication.