| Parameters | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Used by | Network architects, system administrators, and developers | Developers mostly utilize PaaS | End users mostly use SaaS |
| What it Provides | Resources encompassing virtual servers, data storage, and networking components. | Runtime environment, development tools, and middleware | Applications |
| Technical Knowledge | Requires high technical knowledge | Requires basic knowledge | No technical knowledge is required |
| User Controls | Provides authority over the operating system, runtime, middleware, and application data | Grants control over application data | Limited to using the software as provided |
| Scalability | Highly scalable and flexible | Highly scalable for different business needs | Adaptable for all business sizes |
| Use Cases | Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and AWS (Amazon Web Services) | Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine | Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace |
| Level of Control | High level of control over infrastructure and resources | Medium | Lowest |
| Cost | Expensive | Moderately expensive | Least expensive |
Quick Summary
This blog comprehensively analyzes the three primary cloud service models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. It highlights the distinct benefits and limitations of each model, provides guidance for business owners to choose the right one for their specific needs, and highlights the use cases and real-life examples to illustrate the concepts effectively.
Table of Contents
Introduction
The cloud computing landscape is booming, and staying ahead of the competition is necessary to succeed in the constantly evolving IT business landscape. For business owners and decision-makers, embracing the potential of cloud service models has become a pretty strategic move. While the cloud offers numerous opportunities to streamline operations and enhance efficiency, It also aids in fueling growth while reducing the burden of IT infrastructure management, navigating these options can feel extremely overwhelming! If you are unsure which of these models suits your needs the best, we’ve got you covered! But before that, let’s have a data dive!
Stats reveal,
- An estimated 49% of data will reside in public cloud environments by 2025.
- The Global cloud computing market is predicted to reach a staggering $1266.4 billion by 2028, experiencing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.1% from 2023 to 2028.” That’s bigger than the GDP of some entire countries!
- Public cloud services will constitute 46% of cloud infrastructure spending by 2024.
So, whether you’re looking to optimize your existing systems or considering a shift to the cloud, this blog will uncover valuable insights to decide which cloud service model can be the right fit for you.
Cloud Service Models Deciphered: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Let’s go through a detailed analysis of the top three types of cloud computing service models and comprehensively understand them, exploring how they contribute to the dynamic landscape of cloud computing.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS, or Infrastructure as a service, is a key component of the cloud service models that presents users with cloud-based options as an alternative to maintaining physical, on-premises infrastructure. It enables businesses to acquire resources when needed, avoiding higher costs and complexities related to purchasing and managing software. When we talk about numbers, International Data Corporation (IDC) estimates a substantial upswing in adopting IaaS, with a projected annual growth rate of 27.9% by 2026, underscoring its vital role in today’s IT infrastructure landscape.
Well, how does Iaas Work?
In an IaaS setup, a third-party provider hosts and administers various infrastructure components, such as hardware, software, servers, storage, and more, on behalf of their customers. It includes managing essential tasks like system maintenance and backups, ensuring the resilience of the cloud infrastructure, and reflecting the critical importance of effective cloud resource management in sustaining efficient and scalable computing environments.
Characteristics of IaaS
- Virtualization: Utilizes virtual machines for flexible resource allocation.
- Pay-as-you-go: The cost model charges users only for consumed resources.
- Self-Service: Users have control over provisioning and managing resources.
- Network Connectivity: Offers robust networking features for seamless connectivity.
- Storage Options: Provides various storage solutions with scalable capacity.
- Security Measures: Implements security protocols for data protection.
- Customization: Allows users to configure and control infrastructure components.
- API Access: Provides APIs for programmatic access and automation.
- On-Demand Resources: Provides instant access to resources without physical infrastructure setup.
Benefits of IaaS Cloud Computing
Here are a few of the benefits that IaaS cloud computing offers:
🟠 Lower Costs
IaaS cuts costs by letting businesses use computing resources as needed, avoiding upfront hardware expenses, and ensuring efficient spending.
🟠 Enhanced Availability
IaaS allows companies to set up redundant servers quickly and even establish them in different locations to ensure continuous service availability during local power outages and disasters.
🟠 Improved Performance
IaaS providers often operate data centers across multiple geographic regions, enabling IaaS customers to position their applications and services closer to end-users, minimizing latency and maximizing performance.
🟠 Swift Responsiveness
Users can rapidly provision resources, enabling quick testing of new ideas and the speedy rollout of innovations to a broader audience.
🟠 Comprehensive Security
IaaS offers a high level of security both on-site and within data centers, often including robust encryption. This level of security can surpass what organizations might achieve with in-house cloud infrastructure.
🟠 Rapid Adoption of Cutting-Edge Technology
Cloud service providers aim to surpass their competitors by continually offering their users the latest and most advanced technologies. IaaS customers can leverage these advancements earlier and at a reduced cost compared to implementing them on their premises.
IaaS Limitations
The IaaS cloud computing service model has certain limitations, which include:
🟠 Restricted Control over Infrastructure
IaaS providers manage infrastructure, handling maintenance and updates. However, this can result in users having limited control over the environment and may restrict their ability to implement specific customizations.
🟠 Learning Curve
Implementing and managing IaaS solutions, integral to cloud computing service models, may require a learning curve for the organization, especially if they are transitioning from traditional on-premises infrastructure.
When to Opt for IaaS?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), one of the fundamental cloud service models, is suitable for businesses dealing with variable workloads, allowing them to adapt efficiently. IaaS offers high-performance computing resources without costly investments for resource-intensive applications like data analytics. Businesses looking to streamline operations can benefit from IaaS when consolidating multiple data centers or operating globally.
It’s also an efficient software development and testing environment, smoothly integrates into hybrid cloud setups, and assists in controlling IT costs. Furthermore, as a key component of your cloud strategy, IaaS provides reliable disaster recovery solutions and meets compliance requirements for businesses handling sensitive data. For companies aiming to offload routine IT tasks and enhance focus on core operations, IaaS is an apt solution.
IaaS Use Cases
Infrastructure as a Service can be adopted in various sectors. Key utilization areas include:
- Development & Testing: Scalable app development without dedicated infrastructure.
- Web Hosting: Scalable hosting for organizations, adapting to varying traffic.
- Big Data Analytics: Computational power for extensive dataset processing.
- Disaster Recovery: Cost-effective recovery with remote infrastructure replication.
- Storage & Backup: Scalable, secure solutions for data storage and backup.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC): On-demand powerful computing for research.
- E-commerce Hosting: Scalable hosting for online retailers.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Improved web content distribution.
- Collaboration & Communication: Secure, scalable deployment of tools ensuring connectivity in a dynamic business environment.
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI): Remote desktop access for remote work.
- Test & Development Environments: Scalable setups without dedicated hardware.
- Internet of Things (IoT) and AI: Efficient processing and storage for IoT data.
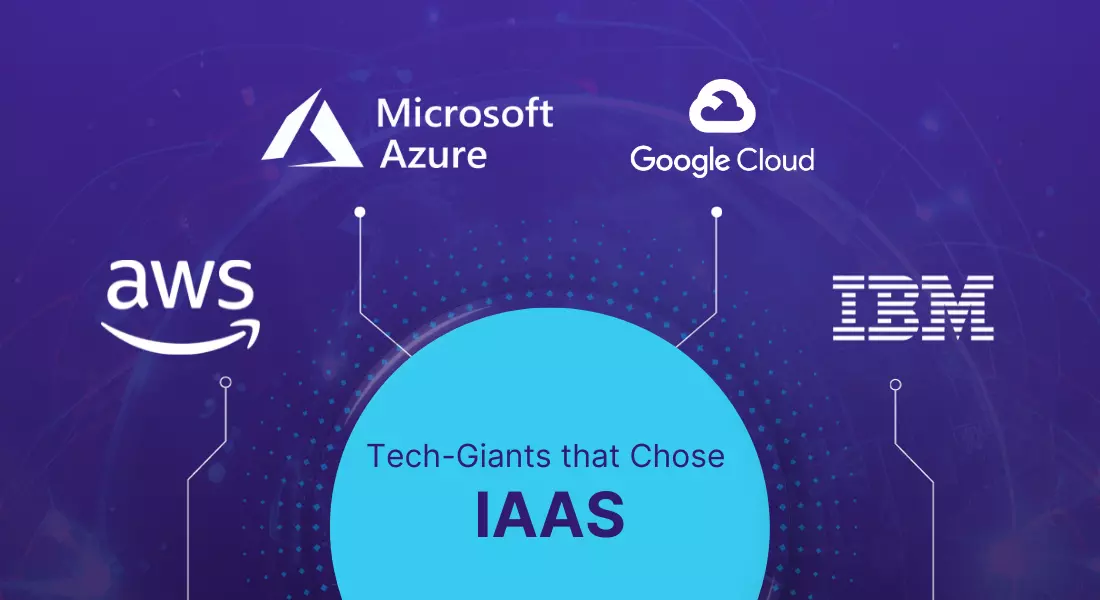
Tech-Giants that Chose IaaS
Several tech giants have embraced IaaS solutions within the cloud service models for their cloud infrastructure needs. Here are a few notable examples:
AWS EC2: Charting IaaS Dominance with 47% Market Share and $80 Billion Annual Revenue
Amazon, a leading public cloud platform, faced challenges in the early 2000s when scaling its online shopping platform. To overcome this, internal tools were created under “Project Dynamo.” Recognizing their value, Amazon launched Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) in 2006, forming the foundation of its Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offering. Today, AWS leads the IaaS market, serving millions and contributing significantly to Amazon’s overall profitability. It empowers businesses of all sizes, fostering innovation and growth across industries, all while keeping an eye on the importance of “AWS cost optimization.”.
Azure’s Winning Formula: A Strategic Brilliance Behind Azure’s IaaS Selection
Azure’s impressive cloud computing platform success isn’t just about offering basic infrastructure (IaaS) and platform-as-a-service (PaaS). It’s about strategically blending these elements with an innate understanding of modern application development trends, particularly the rise of microservices architectures. Critical choices, like prioritizing hybrid cloud solutions for enterprise requirements, have propelled substantial growth, with a market share of around 21%. Strategic partnerships, global presence in 69 regions, and active user engagement further contribute to its success.
IBM Cloud IaaS: Redefining Success in Numbers – A Global Force with 60+ Data Centers
IBM, a global tech giant, strategically employed Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and secured 4-7% of the worldwide market, generating billions in revenue. Operating in 60+ data centers across 19 countries, IBM Cloud IaaS excels in security, compliance, and seamless integration with IBM’s software portfolio. With a comprehensive service suite, emphasis on hybrid cloud solutions, and tangible benefits for clients—including cost savings, agility, and enhanced security—IBM Cloud is a recognized leader showcasing its dominance.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS, or Platform as a Service, is a cloud computing service model providing a virtual space for creating, overseeing, and running applications. It simplifies maintaining and creating the software by offering a comprehensive environment where businesses can focus on building their applications without any worries about the underlying infrastructure. The adoption of this cloud service model is on an upswing, with an anticipated annual growth rate of about 16.74% between 2023 and 2027.
Also, PaaS encompasses supplementary services like security, OS and software updates, backups, and more. PaaS stands out due to its easy-to-use interface. It offers a graphical interface (GUI) that makes it easy for users, especially development and DevOps teams, to collaborate effortlessly throughout the entire application lifecycle. This process encompasses every stage, from coding, integration, testing, delivery, and deployment to feedback.
How does PaaS work?
In this framework, the cloud service provider assumes the responsibility of hosting, supervising, and sustaining all the critical components of the platform, including servers for development, testing, and deployment, the operating system (OS) software, storage, networking, databases, middleware, runtimes, frameworks, and development tools. Users focus solely on building and deploying applications, eliminating the need for infrastructure management. It streamlines development, making the process faster and more efficient.
Characteristics of PaaS
- Development Tools: Comprehensive tools, frameworks, and libraries.
- Automated Deployment: Streamlined deployment processes for faster releases.
- Resource Management: Abstracts infrastructure concerns for developers.
- Collaboration: Facilitates team collaboration with shared environments.
- Cost Efficiency: The pay-as-you-go model reduces upfront and operational costs.
- Multi-Tenancy: Supports multiple users securely on a shared platform.
- Built-in Services: Includes databases, queues, and authentication services.
- CI/CD Support: Enables automated continuous integration and deployment.
- Scalable Architecture: Easily adapts to changing workloads.
- Web App Development: Streamlined coding without infrastructure complexities.
- Mobile App Development: Tools for building, testing, and deploying mobile applications.
- Data Analysis: Scalable frameworks for processing and analyzing large datasets.
- IoT Applications: Handling scalability and connectivity challenges in IoT solutions.
- API Development: Simplified creation and management of application interfaces.
- Content Management: Hosting and managing content management systems effortlessly.
- DevOps Automation: Automating deployment, continuous integration, and delivery.
- E-commerce Solutions: Scalable and secure platforms for e-commerce.
- Collaborative Development: Facilitating efficient teamwork and version control.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Supporting and hosting ERP applications for streamlined business processes.
- Cloud-native development & hybrid cloud strategies: PaaS streamlines development with microservices, containers, Kubernetes, and serverless for consistent deployment across environments.
- SaaS utilizes a web-based, multi-tenancy delivery system: One app, many customers; efficient, private, and cost-effective.
- It operates on a pay-as-you-go subscription model.
- Users benefit from minimal setup requirements and accessibility from any device.
- The service ensures high availability and robust security measures.
- The provider seamlessly manages automatic updates.
- Integration with other platforms occurs smoothly.
- Analytics tools are embedded for data-driven decision-making.
- Data Analytics: Leverage SaaS analytics tools for informed decision-making.
- Finance and Accounting: Employing SaaS financial platforms for accounting and reporting.
- Sales & Customer Relationship Management: Streamline sales processes with SaaS CRM platforms.
- Enterprise Resource Planning: Utilize SaaS ERP solutions for managing core business processes.
- Human Resource Management: Leverage SaaS HRM platforms for employee management.
- Collaboration: Enhance teamwork and communication with SaaS collaboration solutions.
- Project Management: Organizing tasks efficiently using SaaS project management tools.
- E-commerce: Operate online stores through SaaS e-commerce platforms.
- Customer Support: SaaS customer support solutions for efficient assistance.
- Marketing Automation: SaaS marketing automation platforms for automated marketing tasks.
- Learning Management System: Facilitating online training and education through SaaS LMS platforms.
Benefits of PaaS Cloud Computing
Here are some of the benefits offered by Platform as a Service Cloud Service Model:
🟠 Accelerated Time to Market
PaaS empowers development teams to swiftly establish development, testing, and production environments within minutes instead of the weeks or months it typically takes. In today’s fast-moving digital world, speed is essential for companies to market their products and services quickly.
🟠 Low-Risk Adoption of New Technologies
PaaS platforms offer access to the latest resources throughout the application stack. It allows companies to experiment with new operating systems, programming languages, and other tools without requiring substantial investments in the tools and the infrastructure to support them.
🟠 Streamlined Collaboration
PaaS creates a collaborative cloud-based software development environment, providing development and operations teams with remote access to all the essential tools via the Internet.
🟠 Scalability
PaaS allows businesses to scale their application development and deployment as needed. Companies can easily expand their capacity based on demand by building, testing, staging, or running applications. This scalability is crucial for handling fluctuating workloads and growing business needs.
🟠 Reduced Management Overhead
PaaS proficiently shifts the burden of overseeing infrastructure, implementing patches, performing updates, and administrative obligations to the cloud service provider. This reduction in the management overhead within cloud service models allows businesses to focus on their core competencies and application development rather than the complexities of maintaining infrastructure.
PaaS Limitations
🟠 Data Ownership and Privacy
Data ownership and privacy policies in PaaS can limit organizational control over data. In PaaS, data is subject to provider policies, raising concerns about governance and regulatory compliance.
🟠 Vendor Lock-in
PaaS platforms can tie you to specific features, making migration complex and costly. Addressing this limitation is vital for preserving flexibility and minimizing dependencies within the natural dynamics of cloud service models.
Leverage our Cloud Consulting Services for expert guidance and a transformative journey to the cloud.
When to Opt for PaaS?
Businesses should consider adopting Platform as a Service (PaaS) when they strongly focus on application development and must quickly bring new software to market. PaaS is a cost-effective choice, particularly for startups and small businesses, as it eliminates the need for significant infrastructure investments. It is also well-suited for businesses that require scalability to handle fluctuating workloads or anticipate growth. PaaS fosters collaborative development, integrates applications seamlessly, and offers efficient testing and deployment environments, making it a valuable option among cloud computing service models.
PaaS Use Cases
PaaS simplifies development and deployment across diverse scenarios:
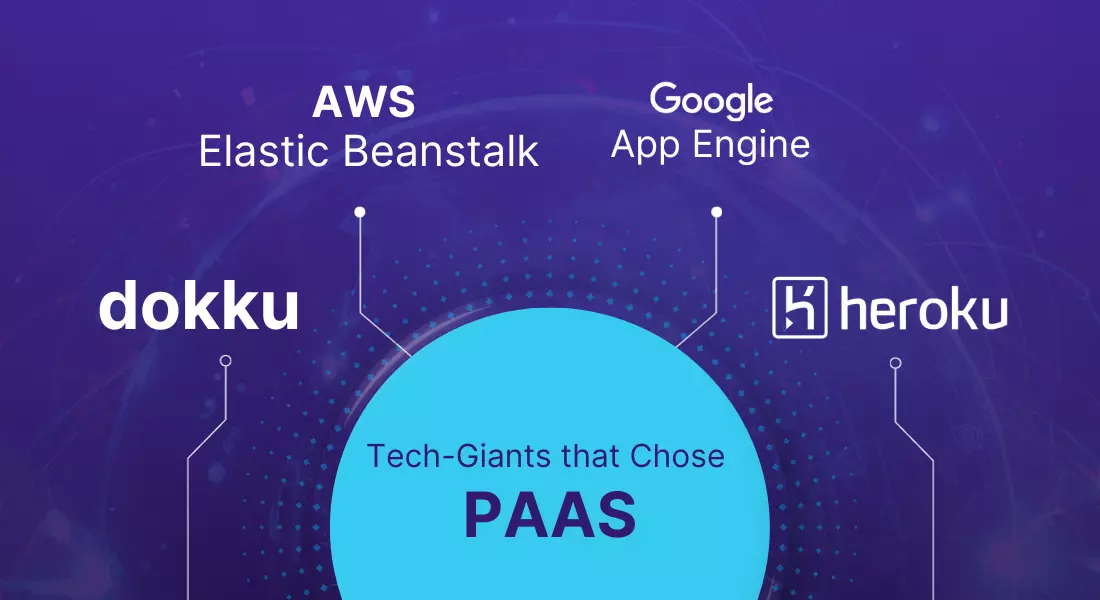
Tech-Giants that chose PaaS
Several tech giants have embraced PaaS solutions within the cloud computing service models for their cloud infrastructure needs. Here are a few notable examples:
Heroku: Elevating Cloud Success with PaaS Brilliance
Heroku, a PaaS cloud platform, enables software developers to build, run, and manage applications efficiently. With cost-effective plans, it supports learning and kick-starts development projects. Boasting 7 million users, including major companies like Airbnb, Heroku’s success stems from continuous growth, a developer-centric approach, technological innovation, a vibrant community, strong partnerships, adaptability, and positive user reviews. Its user-friendly environment positions Heroku as a top choice for cloud application development and management.
AWS Elastic: PaaS Excellence for Exceptional Success!
Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides AWS Elastic Beanstalk as a Platform as a Service (PaaS) offering for application deployment, utilizing a range of AWS services. It integrates seamlessly with AWS developer tools, providing an easy-to-use, flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution. Also, built-in AWS disaster recovery ensures resilient application deployment and abstracts infrastructure management, allowing focus on coding while AWS handles operational complexities.
Google App Engine Soars With PaaS Excellence
Google App Engine (GAE) stands tall as a PaaS success story, emphasizing user-friendly development, serverless efficiency, and seamless integration with Google Cloud. Boasting millions of applications, GAE supports languages like Python, Java, and Node.js, and offers automatic scaling and robust security features. Its impact is seen in reduced development costs, faster time to market, and a thriving developer community. GAE’s journey showcases the transformative power of PaaS, making app development a breeze while achieving scalability, innovation, and efficiency in the cloud landscape.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a prominent cloud service model that gives you easy access to the software over the Internet instead of buying and installing it. You can utilize this fully functional application through a web browser, desktop, or mobile app; you simply subscribe to this service and make monthly or annual payments.
Currently, the market for SaaS is growing and is expected to reach $702.19 billion by 2030. It is pervasive, experiencing extensive daily utilization on personal computers and mobile devices, making it one of the most common cloud computing service models.
How does SaaS Work?
This cloud service model simplifies operations by placing the responsibility of managing essential infrastructure on the service provider. They oversee all the fundamental infrastructure elements needed to deliver applications: servers, storage, network, middleware, application software, and data storage. This empowers business owners to concentrate on their primary activities, alleviating concerns related to IT maintenance.
Characteristics of SaaS
Benefits of SaaS Cloud Computing
Here are the benefits of SaaS service model:
🟠 Minimal Risk
Many SaaS products offer free trials or low monthly fees, allowing users to assess the software’s suitability for their needs with little to no financial risk.
🟠 Time Efficiency
SaaS is quick to set up, and updates are managed by the vendor, reducing downtime and the burden on in-house IT teams.
🟠 Lower Upfront costs and TCO
SaaS lowers upfront costs and Total Cost of Ownership(TCO) by offering subscription-based pricing, eliminating the need for in-house hardware, and providing automatic updates. This scalability without capital expenses and reduced IT staffing needs results in significant cost savings for organizations.
🟠 Flexibility and Accessibility
Users can access SaaS applications from any device with a web browser and an internet connection, promoting productivity perfect for remote work. Also, it ensures everyone uses the latest software version, eliminating compatibility issues and the need for patching.
🟠 Scalability
Adding users or acquiring additional data storage is straightforward, typically involving a simple registration and payment process. This scalability aligns with business growth.
🟠 Reliability and Data Security
SaaS guarantees uptime and automates data backups, ensuring your data’s safety. It also provides better security than traditional software through geographically separated data centers.
SaaS Limitations
Software as a Service (SaaS) offers numerous advantages but has limitations. Here’s a concise overview:
Dependence on Internet Connectivity
Software as a Service (SaaS), a key player in cloud service models, requires continuous reliance on internet connectivity. This dependence can pose challenges in areas with unreliable or limited internet access, impacting seamless access to SaaS applications.
Integration Challenges
In cloud service models, integrating SaaS solutions with existing on-premises systems or other SaaS applications may pose challenges due to compatibility issues.
Subscription Costs
While SaaS eliminates upfront software costs, subscription fees can accumulate over time, potentially surpassing the cost of perpetual licenses.
When should You opt for SaaS?
Companies should consider adopting the Software as a Service (SaaS) cloud service model when they seek ready-to-use software solutions without the complexities of in-house development. SaaS is an excellent choice for businesses looking to access and deploy software applications, quickly reducing time-to-value. Cost efficiency is a key driver, as it eliminates the need for extensive software infrastructure and maintenance, making it suitable for organizations with budget constraints. SaaS solutions also work well for businesses with remote or globally dispersed teams, facilitating easy access and collaboration. As you contemplate SaaS migration, these perks become even more pronounced, offering a smooth transition and optimizing resources.
SaaS Use Cases
Tech-Giants that Chose SaaS
Here are a few notable examples of tech giants who embraced SaaS solutions within the cloud computing service models for their cloud infrastructure needs.
Salesforce’s SaaS Surge with a Remarkable 46% Year-on-Year Growth
Salesforce, a CRM software, experienced an impressive 46% YoY growth, reaching $29.3 billion in revenue for FY 2023. By embracing the SaaS model, it eliminates the need for clients to invest in local software infrastructure, offering scalable and cost-effective CRM solutions on a subscription basis. With a significant 21.7% global CRM market share, Salesforce’s SaaS approach has made CRM accessible to over 150,000 customers.
Zoom’s Skyrocketing Success with SaaS Model in the Cloud
Zoom, a video conferencing platform, adopted the SaaS model, making its services accessible through a simple app download. This shift led to a remarkable revenue increase from $6 million in 2013 to a staggering $4.4 billion in 2023—a 733-fold rise. With 300 million monthly users and a 45% global market share, Zoom’s SaaS success streamlined video conferencing, establishing it as the preferred choice.
Google Workspace: Unleashing SaaS Brilliance with 2B Users and $18B Revenue!
Google Workspace, a cloud productivity suite, attained SaaS success with $18 billion in revenue and over 2 billion monthly users in 2023. With a 27% global market share, it prioritizes accessibility and collaboration. The SaaS model removes installation barriers, and regular updates ensure seamless evolution. Offering a free tier and integration with Google services, Workspace serves businesses of all sizes. Its user-friendly design and scalability make it a major player in the cloud productivity suite arena.
Thus, choosing the right cloud service is essential, but don’t forget about the costs. Keeping an eye on cloud cost optimization is crucial to ensure the service model works well for your business. And, while you have now gained expert insights into the various models, look at our E-book on how to cut costs while optimizing performance.
Shared Responsibility Model
The shared responsibility model in cloud services defines roles in security and management between the provider (CSP) and the customer. It promotes a collaborative approach, with both parties having crucial roles in ensuring a secure and well-managed environment.
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: Comparison Table
Here’s a tabular comparison of the cloud service models (SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS) for your reference:
These were the major differences between various cloud-based service models. Now, let’s explore how we can assist you in selecting the right model that perfectly aligns with your cloud migration strategy tailored to your specific needs and objectives.
Choosing the Right Cloud Service Model: Bacancy’s Expertise
Bacancy is a trusted provider of Cloud Consultancy Services dedicated to assisting businesses by enhancing their operational efficiency by leveraging the potential of cloud technology. Our expertise lies in delivering customized services to unlock the full capabilities of cloud service models.
At Bacancy, we acknowledge that each business is one-of-a-kind, with its particular needs, challenges, and objectives. In our pursuit of selecting the appropriate cloud service model, we closely partner with our clients. It entails dedicating time to gain an in-depth understanding of their distinct requirements and goals. We offer extensive support throughout the journey, encompassing meticulous planning, efficient implementation, workflow customization, and ongoing assistance, including proactive cloud managed services to ensure a seamless and successful transition.
Conclusion
To conclude, IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, which are fundamental cloud based service models, reshape how organizations approach cloud computing. IaaS serves as the fundamental layer, offering extensive flexibility for hosting custom applications and managing data storage. PaaS takes this a step further by simplifying system administration, allowing a more concentrated focus on application development. While SaaS delivers ready-made solutions customized to meet distinct business requirements.
The way these cloud service models work together has changed how businesses operate, reducing the reliance on old-fashioned in-house hosting and moving organizations ahead in technology. However, it’s essential to consider Cloud Services and Solutions to effectively harness these cloud computing models, ensuring that your organization maximizes the benefits of the cloud while maintaining security and efficiency in your operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Yes, cloud providers offer tools and services to facilitate migration between service models.
Security considerations include data protection, compliance, identity and access management, and network security.
Major cloud service providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and others.
Your Success Is Guaranteed !
We accelerate the release of digital product and guaranteed their success
We Use Slack, Jira & GitHub for Accurate Deployment and Effective Communication.