| Parameters | React Native | Ionic |
|---|---|---|
| Created By | Drifty Co. | |
| Platform Supported | iOS, macOS, tvOS, Windows, Web, Android | iOS, Web, Android |
| Tech Stack | Robust JavaScript, and React.js knowledge is required. | Basic knowledge of HTML/CSS and JavaScript is required. Additionally, any available frontend development frameworks, like Vue, Angular, and React, work |
| Functionality | Based on a dynamic runtime approach | Based on WebView Wrapper |
| Performance | Native Performance | Web-based performance with a native wrapper | Development Approach | Native components, JSX syntax | Web components, Angular or React bindings |
| Rendering | Hot reloading features allow real-time rendering | Application refreshes instantly after implementing a change |
| Documentation | Quick basic documentation | Evident and consistent documentation |
| Community Support | Large community, extensive ecosystem | Active community, growing ecosystem |
| Development Cycles | Faster development cycles | Slower development cycles | User Interface | Native-like UI | Customizable UI with Ionic components |
| Code Reusability | The same codebase can be used for Android and iOS devices. Albeit, a tiny piece of platform-specific code might be required. | Use the same code to develop applications for any platform’s devices and OS. |
| CodeTesting | Need a device or an emulator to test React Native efficiently | Testing is executed right in the browser | Learning Curve | The learning curve is steep for beginners with limited flexibility in the tech stack | Ionic is easier to learn as it only requires basic knowledge |
| Use Cases | Facebook, Bloomberg, Skype | MarketWatch, Pacifica, McLaren Automotive |
Quick Summary:
The cross-platform app market is booming thanks to the gracious cross-platform frameworks that enable businesses to cross the threshold and succeed. In this blog, we have presented the quest that aspiring entrepreneurs are stuck with: React Native vs Ionic best cross-platform framework for enterprise app development. Both these frameworks are best as they allow building prototypes and publishing apps with a single source code, so let’s dig in to determine which framework is best, React Native or Ionic, and why.
The blog compares the popular frameworks Ionic and React Native based on parameters such as popularity, architecture, compatibility, framework complexity, developer experience, performance, and more to help you determine which is best for your project.
Table of Contents
Introduction: Ionic React vs React Native in 2024
Several years back, hybrid frameworks, including PhoneGap and Ionic, dominated the cross-platform app development market. To make it easier to create native apps, React Native entered the market. It required separate specialized teams to create and support mobile apps for iOS and Android.
However, Ionic React and React Native take a different route. They enable you to benefit from having a single codebase and produce cross-platform solutions. However, Ionic is a hybrid app framework, so they do not belong in the same category.
Now let’s quickly review the important terminologies before comparing these two mobile app development alternatives.
Native vs Cross-platform for Mobile App Development
There are currently several ways to create a mobile application. Although using native code results in better performance, it has the drawback of involving two teams to work on the product: one dedicated to the iOS ecosystem and the other to the Android ecosystem.
Cross-platform libraries use industry-standard web technologies like JavaScript, HTML, and CSS to simulate native interactions. The hybrid approach accelerates mobile development by using a single project for all platforms and providing a consistent UX across channels.
Following this brief introduction, let’s delve deeper into the most popular tools for creating cross-platform mobile apps: Ionic and React Native.
Introduction To React Native
React Native is a robust framework that enables developers to create native iOS and Android mobile apps faster and cheaper using JavaScript and React instead of building native ones.
The fundamental goal of the React Native framework is to create cross-platform, truly native applications. Objective-C and Swift are the most common programming languages for native iOS and Android apps. React Native started as open-source technology in 2015, and since then, it has grown significantly in popularity. We have also covered a comprehensive article to help you understand why use React Native.

Advantages of React Native
🟠 Irrespective of the platform, JavaScript is used
JavaScript, the most used programming language in the world, is supported by React Native. Additionally, if needed, you can always use native components in Objective-C, Swift, Java, or Kotlin.
🟠 Native-Like Performance
React Native ensures good application performance by rendering code components straight to native APIs.
🟠 Native Looking Interface
The framework includes various UI elements pre-installed, such as buttons, modules, sliders, etc. This shortens the time required for the UI development of apps.
🟠 Hot Reload
This is a beneficial feature that React Native supports. It enables the addition of new releases without causing the state of a program to be lost.
🟠 React Native Community
Looking at the GitHub metrics, you’ll undoubtedly discover that the React Native ecosystem is vast. As a result, you can always find a response to any related query because the developers are happy to share their expertise and learnings when operating with the framework.
🟠 Cost- Effective
React Native is an open-source project that is free to utilize. This makes it a cost-effective choice for cross-platform development, as you can leverage the framework and its libraries without incurring additional expenses.
Negative Aspects of React Native
🟠 Longer Development Period
React Native doesn’t support Write-Once-Run-Anywhere. Each screen or component may need to be specifically developed for each platform, resulting in a more extended development period than frameworks like Ionic. However, this ensures your consumers a genuinely native experience.
🟠 Higher Investments
As React Native development time is longer, you may need to invest extra money. It is essential to consider the potential cost implications when planning your project.
🟠 Use of Native Modules
React Native allows the use of modules written in native languages to perform complicated computations. Developing a complex application may require cooperation with native mobile developers.
🟠 Android App Size
The React Native APK size is more significant than those developed with native technologies of Java or Kotlin.
Introduction to Ionic
Ionic is a hybrid development framework that allows you to create apps using a single codebase. This codebase can be used to build apps for desktops, Web, iOS, and Android platforms. Initially introduced as a free eBook explaining the differences between hybrid and native apps, Ionic enables you to deliver consistent user experience across all channels. It does simplify app development by eliminating the need for separate code bases for different platforms. With the help of Ionic, you can save time and effort while creating apps that work everywhere.

Advantages of Ionic
🟠 Native-looking UI Components
You may create an application that seems native on every platform by using the pre-built UI elements.
🟠 Rapid Testing and Development Cycle
Code can be tested in browsers without loading a complex emulator.
🟠 Learning Curve
There isn’t a big learning curve with Ionic. Knowing Angular, React, or Vue and being familiar with Apache Cordova’s guiding principles are prerequisites for using it.
🟠 Community
The Ionic website claims that 5 million developers have created 4 million Ionic applications. Such popularity guarantees prompt assistance from coworkers in a dedicated Ionic Q&A forum or a Slack channel.
🟠 Pricing
To create apps with a native-like look and feel, the platform provides a free Hobby plan. Ionic Pro is another option with more features for bigger teams. The monthly subscription ranges from $49 to $120.
Disadvantages of Ionic
🟠 Performance Restrictions
Ionic employs web technologies to render apps. When using many callbacks to native code, such a practice has a detrimental impact on the app’s pace and can result in performance problems. Additionally, creating complex visuals or engaging transitions may be difficult. Ionic apps’ performance is consequently inferior to that of native apps.
🟠 Potential Bugs
Each new Ionic version, according to developers, has new issues. Some might be upgrading to the newest releases, using native device features, out-of-date upgrading plugins, etc.
Exploring Similarities: React Native and Ionic
React Native and Ionic are both excellent choices for developing native apps. You can create hybrid mobile apps with Ionic utilizing established web technologies like Javascript and HTML (additionally, web frameworks such as React, Vue, and Angular).
The React framework and Javascript are both supported by React Native, which enables you to create hybrid mobile apps. Regardless of the option you select, you’ll have a single codebase authored in a single language that can be translated into cross-platform mobile applications. All in all, React Native and Ionic accomplish the same task of developing mobile apps. However, they go about it in quite different ways.
React Native vs Ionic: Comparison Table
React Native is learn once, write anywhere approach, whereas Ionic writes once, run anywhere approach. Both Ionic and React Native are a charm for cross-platform app development. It is prudent to look at the circumferential diversification of React Native vs Ionic. So, for your convenience, we have evaluated the same within various parameters.
At Bacancy, we are familiar with React Native and Ionic platforms, as we are using them on a regular basis.
Guided by experience, connect with our cross-platform mobile app expert to make the right choice between native (React Native) and hybrid development (Ionic).
React Native vs Ionic: In depth Comparison
Now that we have understood the basics, Let’s dive into Ionic vs React Native: Head-to-Head Comparison in detail.
Functionality
Functionality is one of the biggest parameters that create a substantial difference among frameworks. Read on to learn the functionality of React Native vs Ionic for mobile app 2024.
React Native uses a dynamic runtime approach and leverages JavaScript to build mobile applications. Through a mobile JavaScript API, the JavaScript code interacts with the native platform APIs of iOS and Android, sending data requests and implementing functionalities. The bridge connecting these two APIs enables React Native applications to resemble native development in behavior and performance.
Ionic incorporates WebView Wrapper, enabling web-based experiences to integrate into native mobile apps. Unlike React Native’s dynamic runtime strategy, Ionic is built on Cordova, which depends on a Webview component or a chromeless browser view. This component utilizes the WebKit/Blink HTML layout engine to render the user interface based on HTML and CSS. Cordova utilizes JavaScript- native bridge to facilitate communication between the WebView application and the native platform. It allows WebView to access native APIs and utilize device functionalities such as the camera.
Verdict: React Native and Ionic make it easy to enhance an app’s native capabilities. Both frameworks support running native code and accessing Native APIs with minimum difficulties for developers.
Popularity
🟠 Over 33K apps were created with React Native, according to research by AppBrain. In contrast, the Ionic framework has created 21K apps.
🟠 Ionic has a market position of 3.72% compared to React Native’s 4.67%.
🟠 If you examine the top applications, 6.38% were created using React Native, while Ionic contributed 0.21% only.
🟠 React Native has a market share of 14.51% and is ranked sixth among all technologies globally by the Stack Overflow Developer Survey 2021. However, Ionic did not reach the top technology list during this poll.
🟠 React Native, which holds a 32% market share, is the second most widely used cross-platform mobile framework, according to Statista. Ionic, which has a 11% market share, is the fourth most widely used cross-platform mobile framework in comparison.
🟠 Ionic has 49.1k stars and 13.6K forks, while React Native boasts 110k stars and 23.4k forks, as per Github.
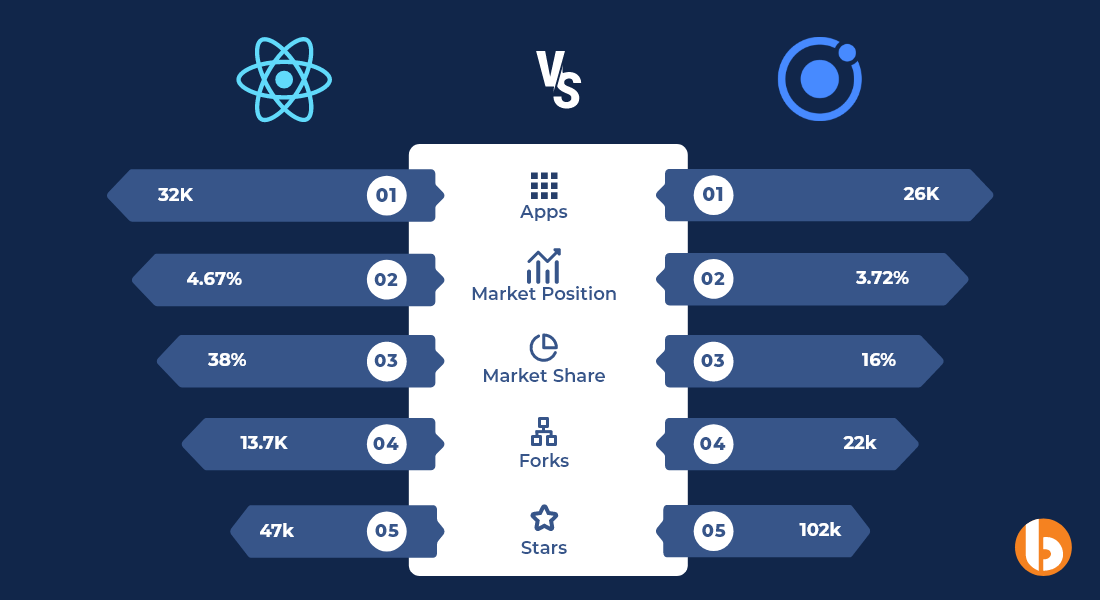
Verdict: React Native is the winner. Undoubtedly, React Native has much greater popularity than Ionic.
Learning Curve
The learning curve for React Native can be steep, especially when you are new to mobile app development or unfamiliar with React and its ecosystem. While obtaining component styles in React Native is comparatively straightforward with its flex layout, you need to understand CSS, ES6, Flexbox, and possibly Redux for state management.
On the other hand, Ionic has a relatively easier learning curve. The installation process is simplified along with npm instructions that include Cordova. Ionic also benefits from its integration with AngularJS providing a comprehensive list of Angular JS extensions and services through the ngcordova element.
Additionally, Ionic offers its online school, Ionic Academy, which offers step-by-step lessons at various levels, making learning more accessible and efficient.
Verdict: Ionic wins this parameter. The grand is much easier, simpler, and fun to learn.
App Performance Comparison
React Native Performance is the ultimate necessity for every framework in the market. Let us compare the metrics of Ionic vs React Native performance.
Boot Time
Boot time refers to the time it takes for an app to load. Both React Native and Ionic generally have comparable boot times. Cold boot times for both frameworks are around 1.5 seconds, while warm boot times are approximately 1 second.
Smooth Scrolling
Contrary to the perception that web-native apps are slower to render, there is not much difference observed in the smoothness of the scrolling between Ionic and React Native. Both frameworks perform their operations within an acceptable timeframe of 16.67 milliseconds, ensuring a smooth user experience with minimal frame drops.
Native Transitions
It is a common belief that when transitioning like “push” and “pop,” web-native apps lose their native feel when the user navigates along the application’s routed paths into a detailed screen and back. But, it is a common belief, not a fact.
The Ionic SDK also falls perfectly into this paradigm. The transitions are not ones that only frameworks that orchestrate native UI controls can accomplish. It is also possible for the web.
Platform-specific or Unified Styling
React Native focuses on achieving a native look and feel using native UI components. It prioritizes platform-specific styling, allowing the app to integrate easily with iOS and Android.
In contrast, Ionic takes a different approach with Adaptive styling and an extensive UI toolkit. It enables your app to adapt to different platforms while maintaining the native feel without requiring complex configurations. Ionic supports both OS-specific styling and brand-centric styling. You can customize the app’s appearance by overriding norms using CSS variables, resulting in greater flexibility.
CPU Consumption and Energy Impact
Ionic and React Native show a noticeable difference in CPU composition. React Native apps strain the CPU more, while Ionic puts less stress on it. Ionic utilizes a faster JS engine called WKWebWiew, while React Native relies on JSCore. Although the impact may not be immediately noticeable regarding app performance, React Natives’ higher CPU usage can lead to faster drainage and reduced battery life. In this aspect, Ionic wins over React Native.
So, How does Ionic stand out in terms of performance?
In contrast, Ionic is cross-platform. It is compatible with online desktop apps built with Electron, iOS, and Android. Compiling a single codebase to serve all these systems with a few minor changes is possible.
How does React Native stand out in terms of performance?
Both iOS and Android are the platforms that React Native targets. Using the same codebase, you may develop an application for both platforms. React Native and React are sufficiently similar to allow you to reuse a portion of the same code when developing a web application with React Native, albeit this has limited application.
Verdict: Ionic is the champ in this area due to its cross-platform compatibility for desktop programs and online apps.
Architecture
The terms “almost native” and “web-first” can be used to describe the architectural distinctions between React Native and Ionic apps.
React Native architecture helps to structure multi-platform mobile applications.
“Nearly native” describes React Native. The underlying widgets are native iOS or Android components, although the applications were created using Javascript and React.
Nevertheless, React Native still needs a Javascript bridge to connect the native components to the compressed Javascript and React code. Therefore, it’s not truly a native app. React Native is an abstraction that fully controls the platform’s UI modules. React Native apps closely resemble native apps in appearance and feel because all of the Interface components are native to the framework.
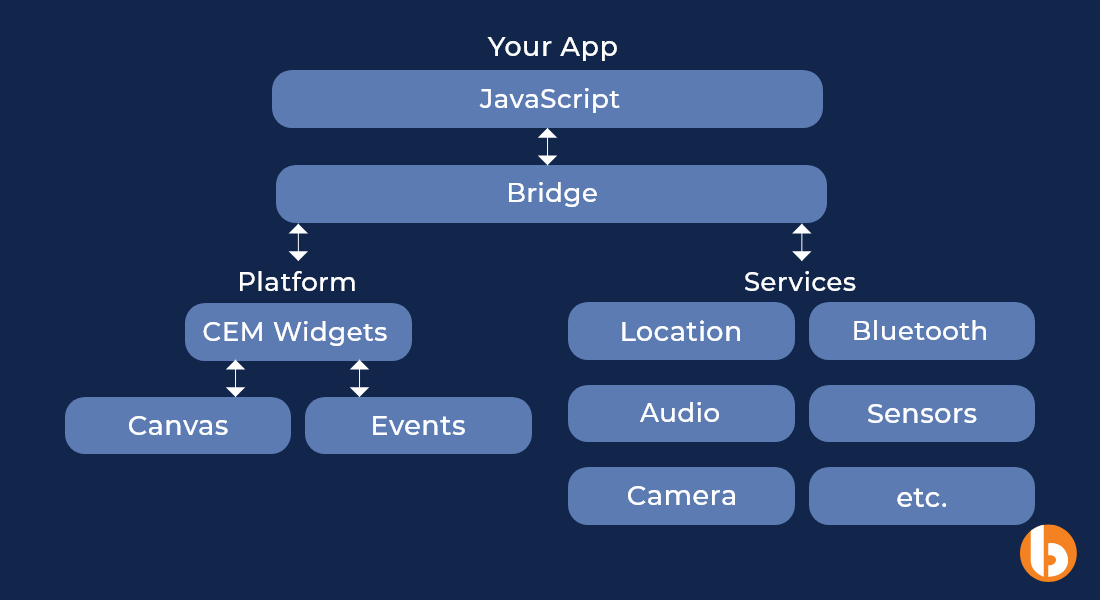
The ionic architecture allows building web, cross-platform mobile, and desktop apps with one shared code base.
One is just a wrapper that accepts HTML, CSS, and Javascript code and puts it into a WebView to develop mobile applications. Technology like Cordova or Capacitor connects the WebView to the Ionic codebase at runtime. An Ionic application is just a mobile website turned into a mobile application.
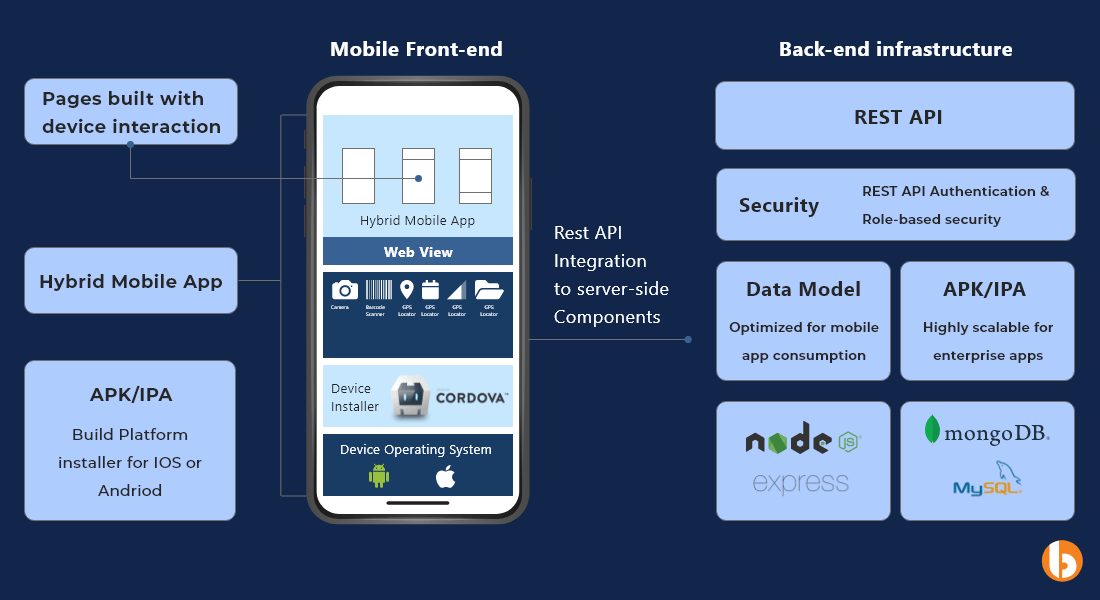
React Native vs Ionic Architecture Verdict: React Native is ideal for native app-like features. Ionic is suitable for mobile apps aligned with website design or built using a web framework. Choose based on project constraints and software needs.
Language Stack
React Native: Engineering with JavaScript and React.JS
It uses JavaScript, a popular high-level, dynamic programming language. Product owners can also write modules in Objective-C, Swift, or Java languages depending on their needs.
Ionic: Develop with a Superset of JavaScript – TypeScript
The Ionic framework uses web technologies like JavaScript, HTML5, and CSS to build apps and assists product owners in transcribing the language quickly. It needs a Cordova wrapper for accessing native platform controllers. The core of Ionic is written with Sass and relies on the Angular framework.
The primary programming language of Ionic is TypeScript, a JavaScript superset that compiles plain JavaScrip. TypeScript enhances code quality and spots and removes mistakes during typing. But TypeScript is optional, and you can also use JavaScript directly.
Running Code and Performance
React Native renders code components to native APIs using the JSVirtual Machine. iOS entails JSCore by default, but VM to Android is installed additionally. React allows using native iOS and Android, non-reusable modules across two platforms to accomplish tasks not covered in cross-platform JavaScript APIs. It also assists in delivering better performance for image editing and video playback.
It needs bridge APIs for both Android and iOS to connect with native modules. The remaining codebase is available across platforms. React Native apps can share approx upto 90 percent of JavaScript Code. The Native libraries also contribute to enhancing performance. React Native uses JIT compilation for Android but doesn’t provide AOT for iOS. For iOS, it doesn’t compile but interprets the JS code.
Wondering why React Native has been ruling the cross-platform mobile development market for quite some time now?
Hire React Native developer from us who are well-versed at fulfilling the varying parameters such as security, scalability, reliability, user experience, testability, and so on.
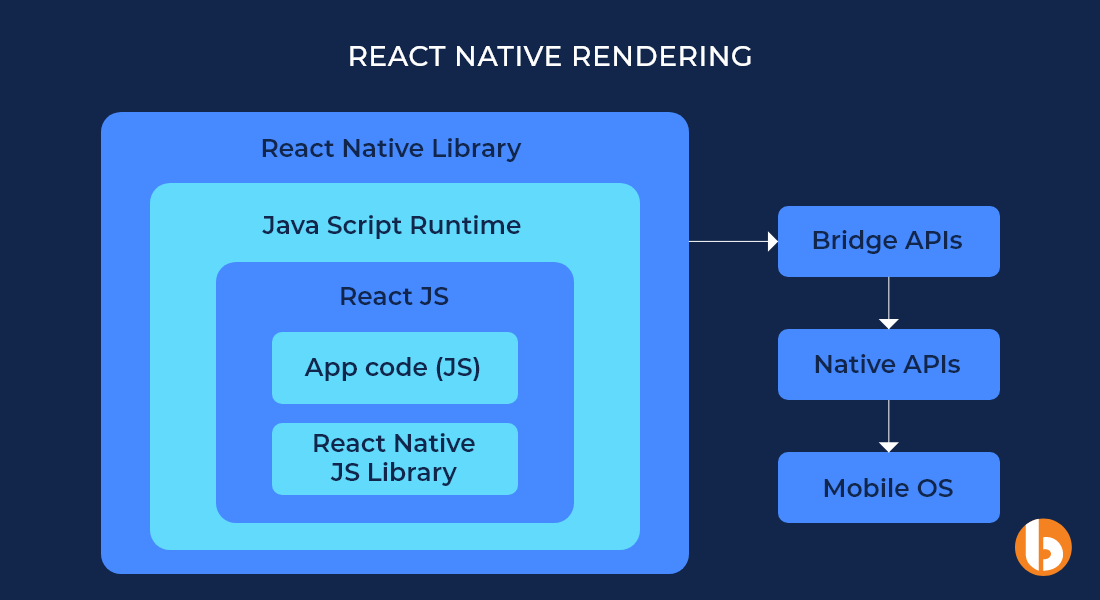
Ionic stands behind React Native in performance as it uses web technologies to render an app which affects speed. It also doesn’t use native components, and it uses the native wrapper, Cordova, to connect with the native API and adapt app behavior to the underlying platform. Ionic has several components available by default which reduces development time.
It also has a fast testing process and can run directly in a browser. Ionic uses JIT compilation for Android, but for iOS, it is impossible; WKWebView (a platform browser, as default for iOS) supports JIT, so it uses embedded web content in the app. It also provides JIT conversion of JS code to machine code, improving rendering performance.

Verdict: If we compare the performance of React Native vs Ionic, though both are exceptional in terms of their code rendering and performance React Native leaves Ionic far behind when it comes to complex and rich apps.
Coding, Building, and Debugging
Both React Native and Ionic offer similar capabilities for coding, building, and debugging mobile apps. You can utilize popular code editors such as WebStorm, Visual Studio Code, or ALM for writing and debugging. React Native suggests using iOS and Android emulators to stimulate device behavior for testing.
IDE options with JavaScript ES6 support for coding include Visual Studio Code, Atom, WebStorm IDE, ALM IDE, and Angular IDE. Some are free, while others have paid features.
Debugging can be done through the Chromes browser’s tools, allowing you to inspect and trace JavaScript code. Android development requires installing Java JDK, Android Studio and updated SDK tools.
For iOS, you need Xcode on a Mac, an iOS device, and an Apple ID (or a paid Apple Developer account).you have various tools available for coding, building, and debugging mobile apps using Ionic and React Native. Choose an IDE or code editor that suits you, and utilize browser tools and emulators to debug specific platforms.
Framework Complexity
Given that Ionic apps may be created using a variety of web frameworks, it is tough to distinguish the intricacy of React Native and Ionic properly.
It will be simpler for you to master Ionic if you have experience with web development because you will be using standard web technologies. Besides that, if you are familiar with Javascript and the web-based React architecture, learning React Native won’t be difficult.
Verdict: Ionic and React Native have relatively similar levels of difficulty. Both of them primarily employ Javascript as a programming language. However, a developer will probably feel more at ease developing with Ionic because it employs standard web technologies.
Documentation
One of the most crucial components of a developer-friendly framework is documentation. You can quickly solve difficulties and discover answers to their inquiries with the help of clear documentation.
Ionic and React Native both offer excellent documentation. Even editable code examples with outputs are included in React Native’s documentation. Ionic’s documentation also makes up for its lack of editable code samples with the breadth of information offered. Even best practices for integrating your preferred web framework into Ionic are included in the documentation for Ionic.
Verdict: This parameter is a tie because both frameworks have top-notch documentation.
Developer Experience
As a mobile developer, you’ll feel more at ease with the React Native development expertise because it’s similar to natively designing an app. As a web developer, you will feel considerably more at ease using the Ionic programming environment.
Verdict: It comes down to personal opinion about which framework offers the best development experience. If you run into trouble, both frameworks have excellent documentation and a wealth of resources.
Cost of Development
Both models provide cost and time-saving benefits from a business standpoint. Ionic is, nevertheless, significantly less expensive than React Native when comparing the two frameworks.
Ionic enables you to create hybrid apps running on several platforms by only creating the app once and using a single codebase. Although React Native is free, hiring a skilled React Native developer might save you money. The cost of hiring React Native developers starts from $20.
On the other hand, depending on the functionality, you can choose between the open-source and premium versions of Ionic. Ionic has three different pricing tiers: Basic ($499/month), Standard ($2499/month), and Enterprise ($5999/month) (custom pricing).
Verdict: React Native wins as a preferred choice for creating top-notch apps that closely resemble native experiences, despite the significant investment required in both Ionic and React Native.
Ready to harness the power of React Native?
Partner with the leading React Native App Development Company like us and unlock limitless possibilities for your app! Build an exceptional cross-platform solution that delights users and maximizes your business potential. Get in touch with us today!
When to choose which?
Consider these factors to choose React Native or Ionic Native based on your specific project requirements and development expertise.
React Native is Preferred When:
- You’ve already implemented React Native into your website or application.
- Your development team is a React guru.
- Your project’s reliance on native platforms is crucial and significant.
- You have the resources and time to build your project.
- You already have sufficient funds or a flexible budget to cover the high development costs.
Ionic Native is a Suitable Option When:
- You plan to develop Progressive Web Apps (PWA).
- You want to employ web development capabilities to deliver a web and mobile experience.
- You are seeking a framework that will guarantee future high performance.
- You desire to create and expand enterprise-level, mission-critical apps.
- You have experience in web programming and want to create an app for entrepreneurs.
Conclusion
In the battle of React Native vs Ionic, both have demonstrated their potential and promise as cross-platform app frameworks. Each framework offers a unique advantage and ongoing development, ensuring exciting advancements and enhanced functionality over time. Ultimately the choice between React Native and Ioinc will depend on your specific needs and requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Both React Native and Ionic have a sizable community, considerable acceptance by major corporations, and widespread customer use of mobile applications.
Both each have distinctive qualities and diverse environments. Both serve distinct purposes and prove to be advantageous in a slew of instances. To further comprehend how Ionic and React Native function and the benefits and drawbacks of each, refer to the content above.
Ionic integrates well with a workforce that is unfamiliar with native systems because it uses web technologies (HTML, CSS, and JavaScript).
You will be able to create fantastic mobile applications using Ionic and access native features like GPS, maps, or audio. With the same time and knowledge needed to construct a website, these functionalities are prepared for deployment into the Play Store and App Store.
The development of React Native is simple for programmers who have experience with iOS or Android. In comparison to Ionic, the learning curve for a React programmer to comprehend and troubleshoot a React Native application is larger.
React Native, on the other hand, has the shining accomplishment of being able to access the native features of mobile devices, giving your mobile application a more native appearance and experience.
Using JavaScript as the primary language, both enable programmers to develop mobile apps that can operate on several platforms. Ionic’s strategy is more “web-like,” nonetheless. This means that in order to access native functions, the program executes on a web browser that is encased in an SDK.
React Native exchanges data by sending signals to 3 bridges: the UI Thread, Layout Thread, and Javascript Virtual Machine.
Ionic and React Native have fairly similar levels of difficulty. Both of them primarily employ Javascript as a programming language. However, a developer will probably feel more at ease developing with Ionic, because it employs common web technologies.
Your Success Is Guaranteed !
We accelerate the release of digital product and guaranteed their success
We Use Slack, Jira & GitHub for Accurate Deployment and Effective Communication.