Table of Contents
Introduction
Recently, our python team participated in a seminar where the tech enthusiasts discussed Python and the top-notch Python libraries used for data analysis, machine learning, and data science. NumPy was one such python library that was discussed the most. It is used for handling complex mathematical operations, data analytics, and machine learning. The seminar covered the application of NumPy in various domains such as python programming.
In today’s Python with NumPy tutorial, we will learn about NumPy and look at some practical applications of methods facilitated by it. Some of you might not be familiar with NumPy and how to work with it. We are here to help you. After going through our tutorial, your doubts will be solved.
What is NumPy?
NumPy is a python project available in open source made to enable complex numerical computing in Python. It was created in 2005 to include functions for handling tasks belonging to the domains like matrices, Fourier transform, and linear algebra.
NumPy simply implies Numerical Python. Being an open-source project, the whole source code for the NumPy library is available on github.
Why use NumPy?
Python consists of lists that serve the purpose of arrays. But, lists are slower to process. NumPy focuses on providing array object that is almost 50x faster than the default Python lists. NumPy provides an array object called ndarray. The supporting functions provided by NumPy make working with ndarray preferable over traditional Python lists. Arrays are continually used in the domains like Data Science and Machine Learning due to the importance of their requirement for speed and resources.
Advantages of NumPy
The major benefits of using NumPy and arrays over traditional Python lists are:
- Greater speed: In the background, NumPy uses algorithms written in basic C language, causing their execution to complete in nanoseconds rather than seconds.
- Reduced dependency on loops: NumPy helps to alter the dependency on loops preventing programmers from getting jumbled in the nest of iteration indices.
- Better quality: Being an open-source project, NumPy has thousands of contributors working to make NumPy bug free, faster, and friendlier.
- Cleaner code: While dealing with complex mathe/matical or numerical operations, a code without loops will look like the equations you are trying to calculate.
Python with NumPy: Prerequisites & Tech Stack
We assume that you have prior knowledge of the following.
- Python3 Programming
- Virtual environments
- Conda/pip
- Google Colaboratory/Visual Studio Code Editor
To get started with this tutorial, make sure you have the following.
- Python
- IDE (Google Colaboratory or Visual Studio Code)
We will be using the following technologies.
- NumPy
- Google Colaboratory/Visual Studio Code
Let’s start exploring various use case applications of NumPy. Here’s my system setup:
- Ubuntu 20.04 OS
- Python 3.8+
Install NumPy Using pip
Install numpy package using pip (recommended to do so inside a virtual environment to avoid polluting your OS).
Create New Directory
Create a new directory and navigate to it using the below commands.
While the above steps should be all that you need to get started with numPy and python, there are a couple more tools that you may optionally install to make working with data science libraries more developer-friendly. These tools can be any of the following.
- IPython
- Jupyter Notebook
- VS Code
- Google Colaboratory
For demonstration, we will be using python notebooks in VS Code editor.
Discover skilled python developers, Not development worries!
Put forward your requirements and we will help develop your product. Bacancy’s experienced developers are for you! Contact today and hire Python developers.
Python with NumPy: Getting Started with NumPy
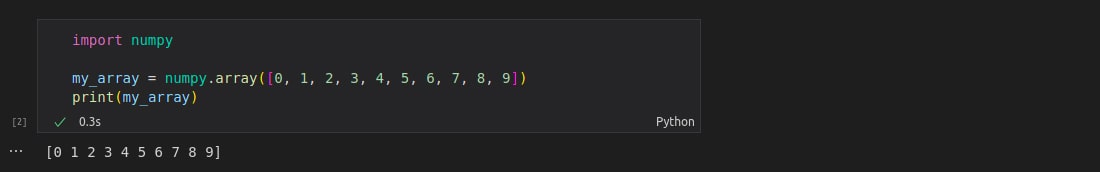
Let’s start by using the basic data type offered by numPy, i.e., numpy array. And for that, let’s start by importing the numPy package.
Output:
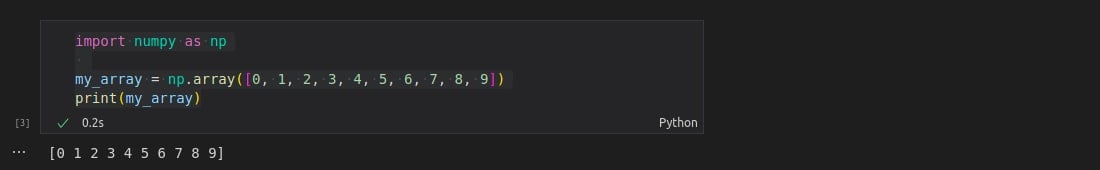
Now, for convenience, numPy is usually imported with “np” as its alias.
*Note: Alias is an alternate name given to anything.
Output:
Application-based Introduction to NumPy Arrays
Moving further in Python with NumPy tutorial, let’s start our core application using NumPy arrays.
Create NumPy Array
The major reason to use numPy in data science and machine learning applications is the need to work efficiently with arrays. Numpy provides array objects called “ndarray.”
A numpy function “array()” can be used to create an array.

import numpy as np blank_array = np.array([]) print(blank_array) my_array = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]) print(my_array) print(type(blank_array))
Output:
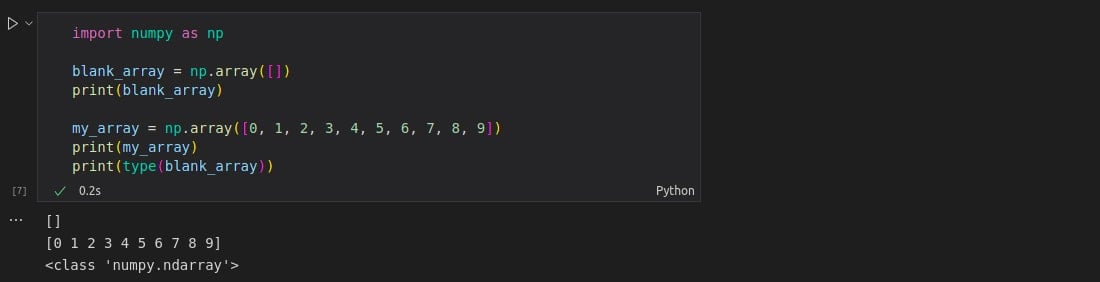
*Note: A numpy array expects an object to be passed with the “array()” function. It returns a syntax error if no object type argument is passed with the function.
The “array()” function can be used by passing any array-like object into its argument like a list, tuple, etc.
Dimensions in Array
Arrays can be categorized concerning their dimensions.
0-D Arrays
0-D arrays can also be called scalars. Every element of an array is itself a 0-D array.
1-D Arrays
1-D arrays can be considered an array consisting of multiple 0-D arrays as their elements. 1-D arrays are also called uni-dimensional arrays, the most basic and commonly used arrays.
2-D Arrays
2-D arrays are the arrays that consist of 1-D arrays as its elements and are often used to represent matrices.
3-D Arrays
3-D arrays are the arrays having matrices (2-D arrays) as its elements.

import numpy as np
zero_d_array = np.array(23)
print("0-D ARRAY", zero_d_array)
one_d_array = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3])
print("1-D ARRAY", one_d_array)
two_d_array = np.array([[0, 1, 2], [9, 8, 7]])
print("2-D ARRAY",two_d_array)
three_d_array = np.array([[[0, 1, 2], [9, 8, 7]], [[0, 1, 2], [9, 8, 7]]])
print("3-D ARRAY",three_d_array)
Output:
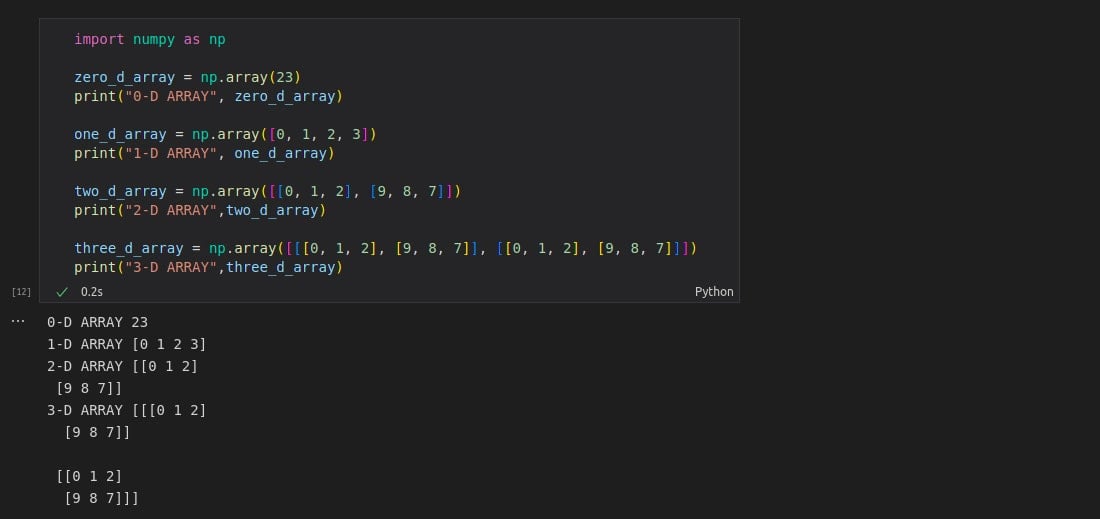
Higher Dimensional Arrays
Arrays in Numpy are not limited to having only three dimensions. An array can have any number of dimensions and can be created using the “ndmin” argument to define the number of arguments in the array.

import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], ndmin=4)
print('no. of array dimensions :', my_array.ndim)
print(my_array)
Output:
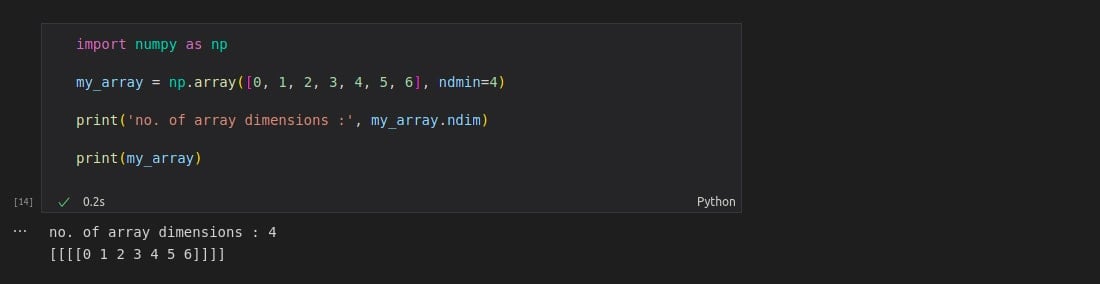
Here, with the “ndmin” argument, it can be seen that it supports arrays with any number of dimensions. In the above case, the 4th dimension, the innermost dimension, has seven elements.
Array Indexing in NumPy
In Python with NumPy Tutorial, the next section is about array indexing in NumPy. Array elements can be accessed using array indexing. Any array element can be accessed by using its index number. Also, it should be kept in mind that, like any other arrays, numPy arrays also have indices starting with 0. Therefore, the first element will always have an index 0, and the second element will have an index 1, etc.
Elements can be accessed using array indexing for various purposes like accessing the elements, using the elements for various mathematical operations, etc.

import numpy as np
one_d_array = np.array([9, 8, 7, 6])
print("First element: ",one_d_array[0])
print("Second element: ",one_d_array[1])
print("Addition of first 2 elements: ",one_d_array[0] + one_d_array[1])
two_d_array = np.array([[8,7,6,5], [4,3,2,1]])
print("3rd element of 1st row: ", two_d_array[0,2])
print("4th element of 2nd row: ", two_d_array[1,3])
Output:
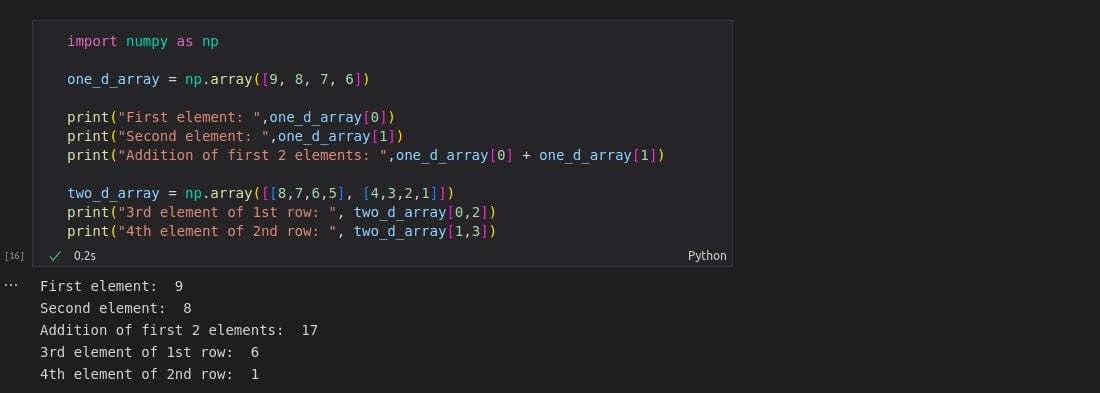
Access Elements in 3-D Array or Other Higher Dimensional Arrays
When it comes to accessing elements in 3-D arrays or other higher dimensional arrays, it becomes a little complex. One should make sure to understand the structure or the dimensions of the arrays before manipulating them. Taking the example of 3-D arrays here:

import numpy as np three_d_array = np.array([[[9, 8, 7], [0, 1, 2]], [[7, 8, 9], [5, 4, 3]]]) print(three_d_array[1, 0, 2])
Output:
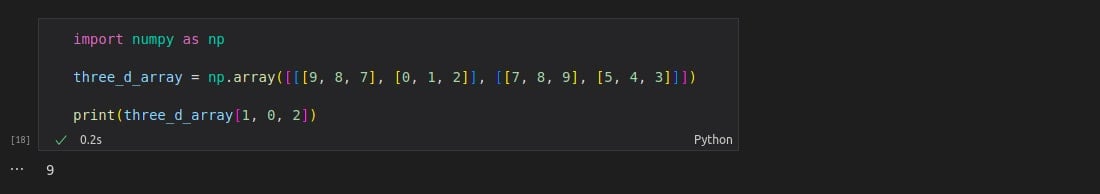
Let’s try to understand the last line in this piece of code.
Here,
three_d_array[1, 0, 2] is printing the value 9.
The reason for the same is that the first number represents the first dimension that contains two arrays:
[[9, 8, 7], [0, 1, 2]] and [[7, 8, 9], [5, 4, 3]]
Since we have selected index 1, we are left with the second array:
[[7, 8, 9], [5, 4, 3]]
The second number represents the second dimension, which also contains two arrays:
[7, 8, 9] and [5, 4, 3]
Since we selected index 0, we are left with the first array at index 0:
[7, 8, 9]
Now, the third number represents the third dimension, which contains these three values:
7, 8, and 9
Since we selected index 2, we end up with the final value:
9
Negative Indexing
Negative indices can also be used to access array elements from the end.

import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([[1,2,3,4,5], [6,7,8,9,10]])
print('Last element from 2nd dimension: ', my_array[1, -2])
Output:
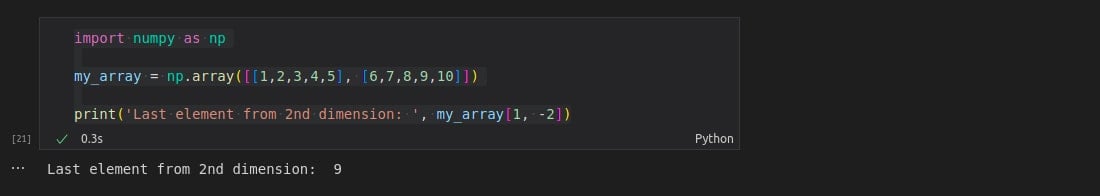
Here, it can be seen that the output is element 9.
The reason for this is that the statement “my_array[1, -2]” accesses the second array of the dimension using the first index value set to 1, that is
[6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
And then, the second index value set to -2 accesses the element at the second index from the end.
9
Conclusion
So, I hope Python with NumPy tutorial was helpful for you. For more such tutorials to explore python, visit the Python tutorial page and start learning. Feel free to connect with us if you have any queries or suggestions.
Your Success Is Guaranteed !
We accelerate the release of digital product and guaranteed their success
We Use Slack, Jira & GitHub for Accurate Deployment and Effective Communication.